
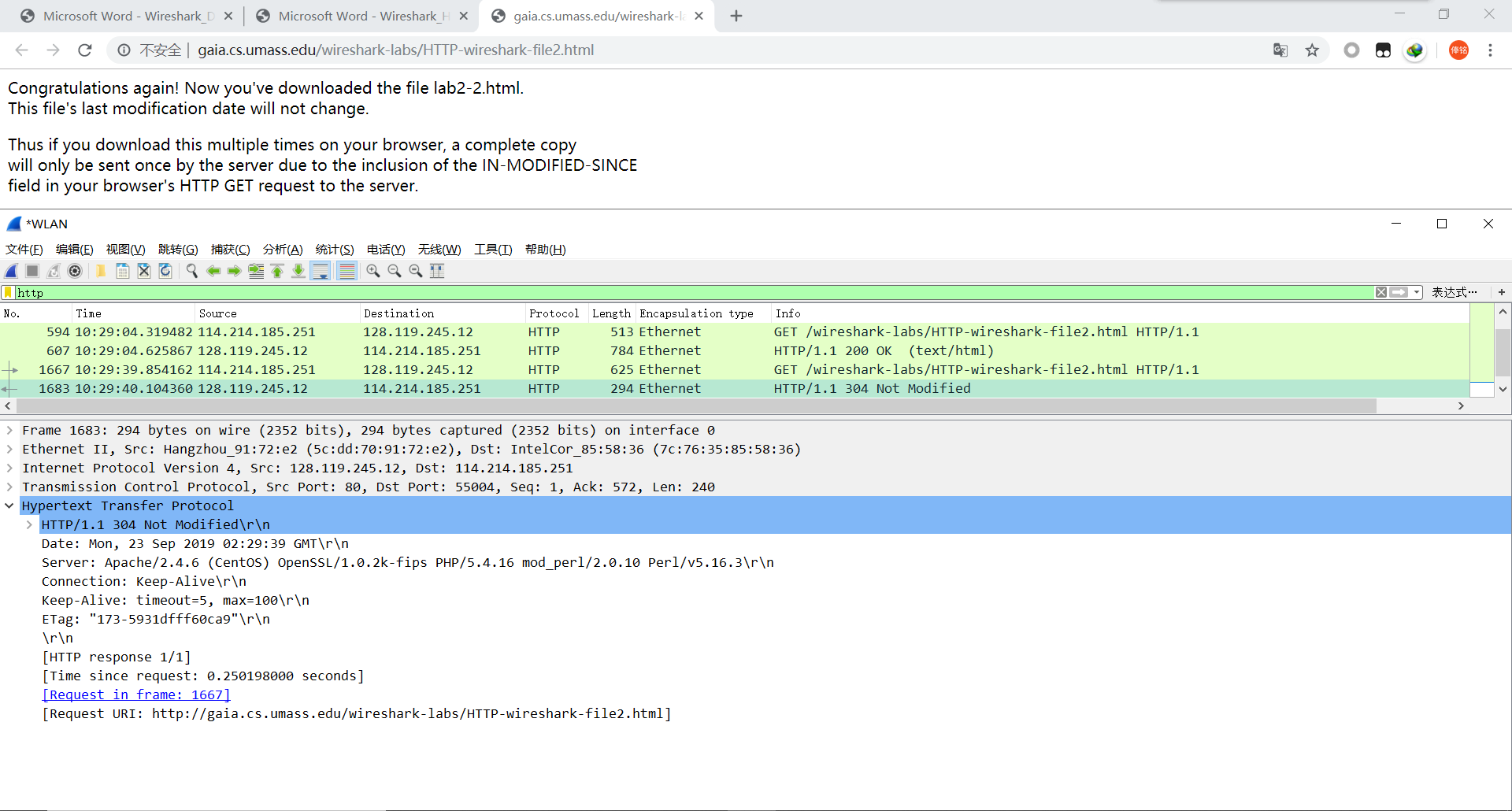
For example, 200 means that the request was accepted properly, whereas 404 indicates that the requested resource was not fond on the server. Some of the common status codes are listed here. When the server responds to a command from a client, it sends along a numerical status code for the response. Other commands are defined, but they are generally not used very often. GET is used to request a webpage from a server, and POST is used to submit information back to the server, usually as part of a form on the website. The two most common HTTP commands are GET and POST. Since HTTP is a text-based protocol, it defines a set of commands and responses to make it easy for the system to understand each packet.

In fact, if you look at the address bar of most web browsers, you’ll still see in front of web addresses, indicating that it is using the HTTP protocol to access that site. HTTP is the protocol used to access webpages on the World Wide Web. As with many early application-layer protocols, it is actually a text-based protocol, making it very easy to read and work with manually if desired. HTTP itself is an application-layer protocol that is built on top of the TCP transport-layer protocol. HTTP was developed by Tim Berners-Lee while he worked at CERN in the late 1980s as part of his project to build the World Wide Web. One of the most common of those is the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, or HTTP.
Next, let’s review a couple of application layer protocols.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
